Okay so now that you have a directory and c++ file created in CS50 IDE (if not see here how to do so,) we are going to look into how we can create a basic piece of coding that with take an input from a user and read out some text. To start the code we’re going to want to include some libraires (#include <iostream>) and specify a namespace (using namespace std;) that will just make the code able to work with the correct data, as well as make the code easier to write.
Code 1.
Write a code that will display a greeting “Hello” to the user.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "Hello" << endl;
return 0;
}- Copy and paste this into your c++ file you created on the last page (example_1.cpp (to open this click on it in the left hand menu)).
- Now to run this code it first needs to be compiled. If you are using CS50 then it has an inbuilt compiler called g++ other coding envirnoments may need an external compiler. To compile our code type (g++ example_1.cpp -Wall) into the terminal. If no error messages occur then your code has been compiled successfully, if you have error messages ensure that everything is spelled correctly and the right symbols are all in place.
- Once you have compiled you can run the code by typing ./a.out into the terminal. This can be changed by giving the code a name whilst compiling. For example if comiled as g++ -o example example.cpp -Wall, you would the call it with ./example. Note the ./ is required to call the function
g++ example_1.cpp -Wall./a.out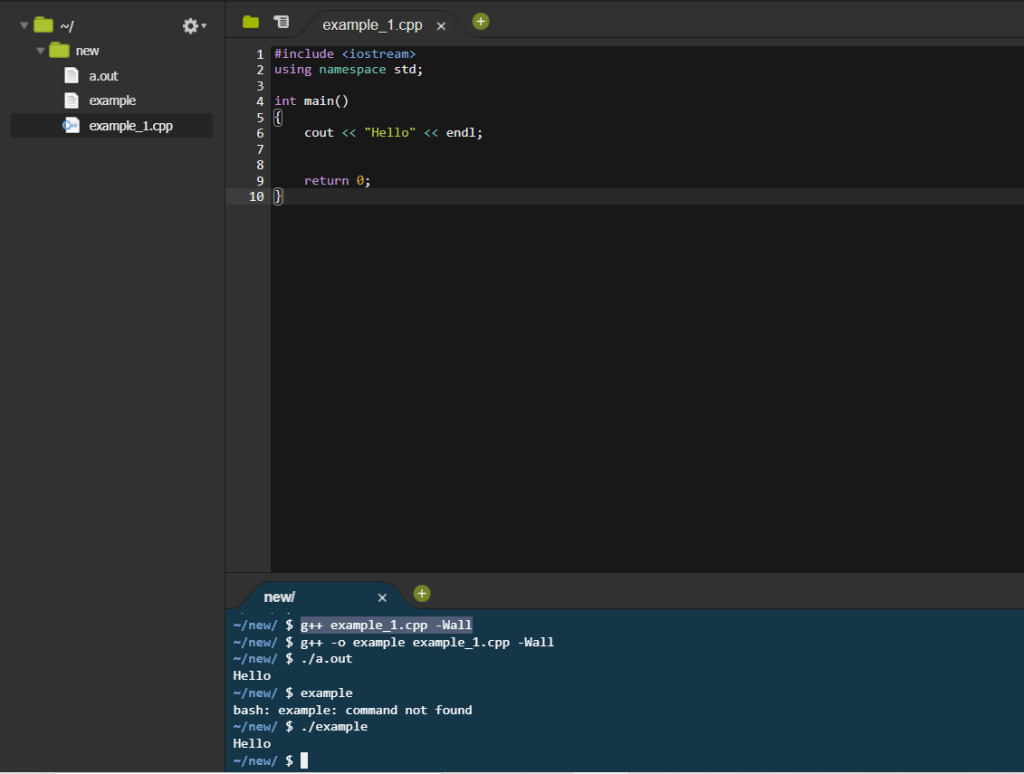
Code 2.
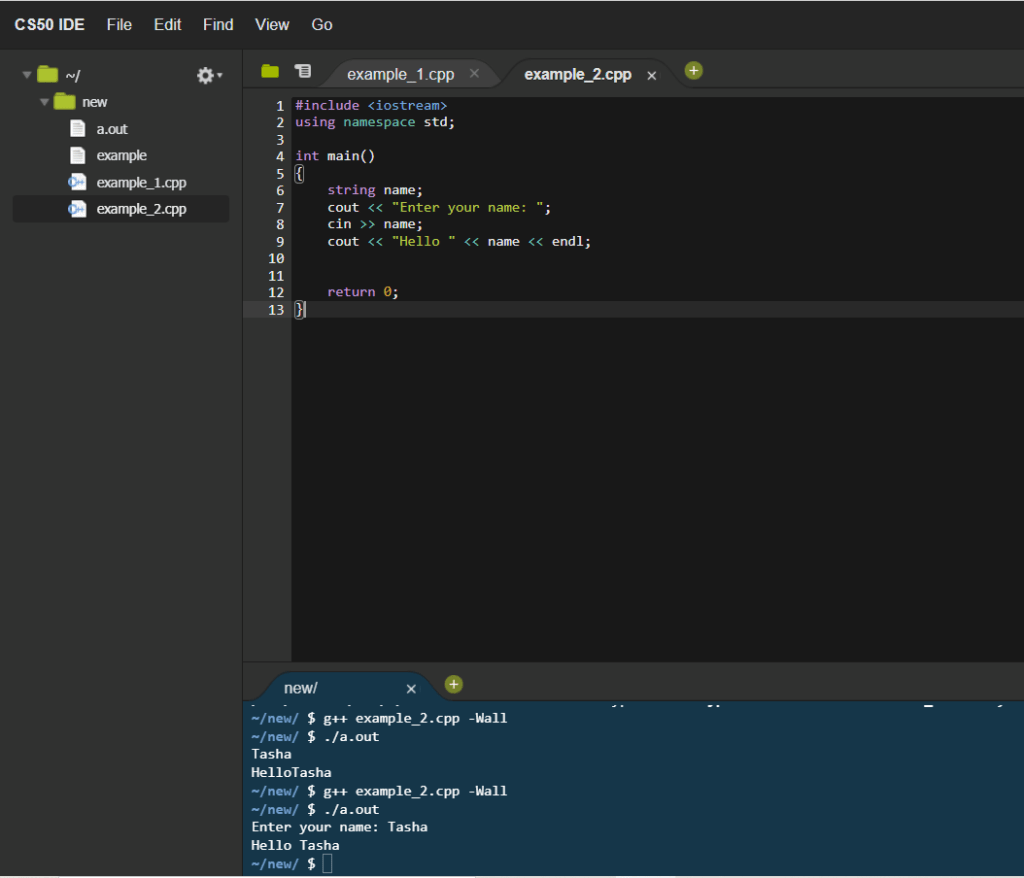
Write a code that will take an inputted name and print “hello name”.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string name;
cout << "Enter your name: ";
cin >> name;
cout << "Hello " << name << endl;
return 0;
}
Code 3.
Write a code that prints out a person’s inputted name and age.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string name;
int age;
cout << "Enter your name: ";
cin >> name;
cout << "How old are you? ";
cin >> age;
cout << "Hello " << name << " you are " << age << " years old." << endl;
return 0;
}
